Devereaux et al. ran an RCT comparing dabigatran vs. matched placebo. Patients were supposed to take the drug daily for 2 years. Analyses were done according to the intention-to-treat principle (ITT).
Notably, the study drug was permanently discontinued in 401 (46%) of 877 patients allocated to dabigatran and 380 (43%) of 877 patients allocated to placebo. This is the highest non-adherence rate I have ever seen.
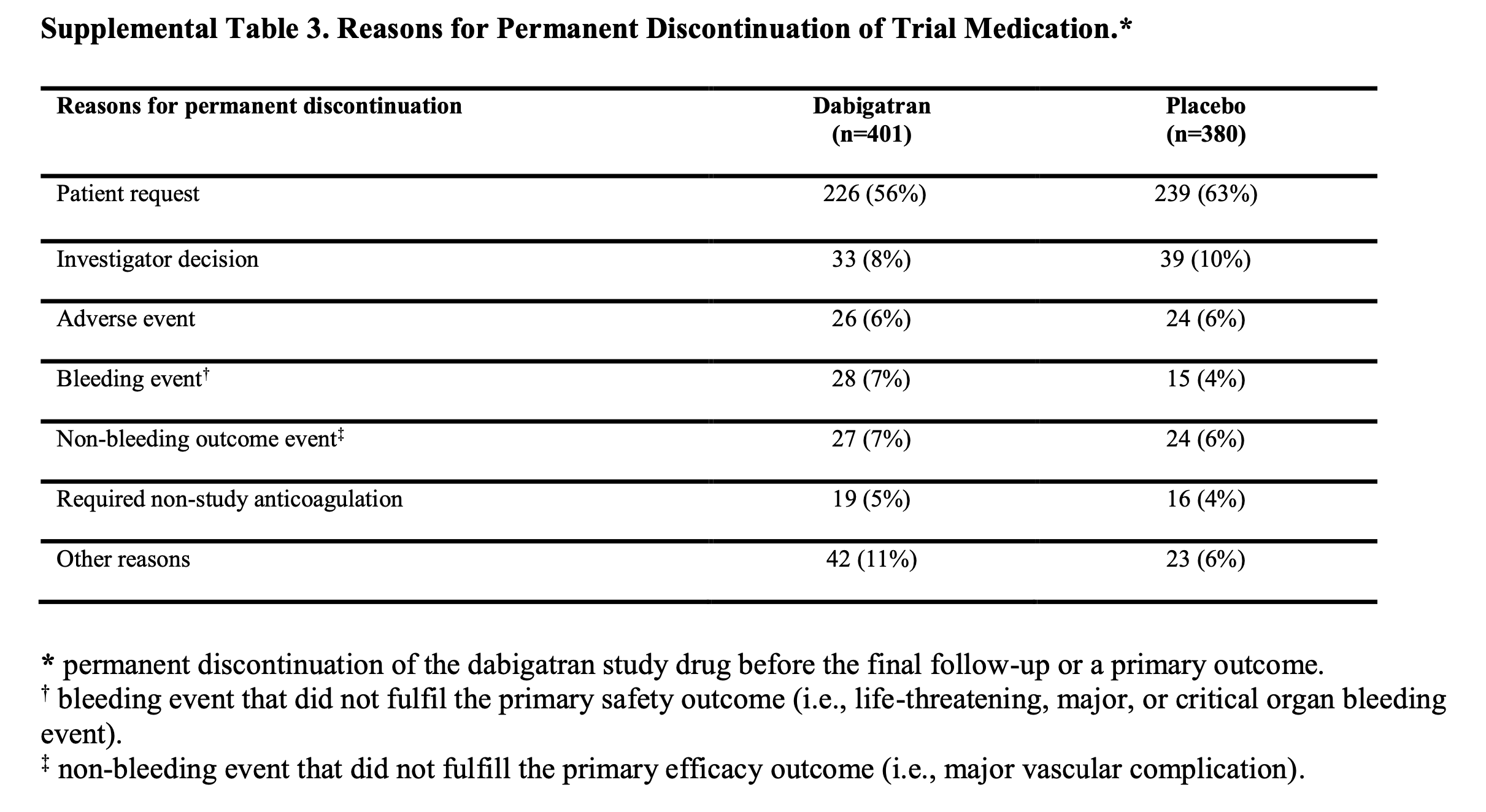
Among patients who permanently discontinued study drug, the median time that patients took the drug was 80 days (IQR 10–212 days) in the dabigatran group and 41 days (6–208) in the placebo group. Among patients who did not permanently discontinue study drug, the median time that patients took the drug was 474 days (237–690) in the dabigatran group and 466 days (261–688) in the placebo group.
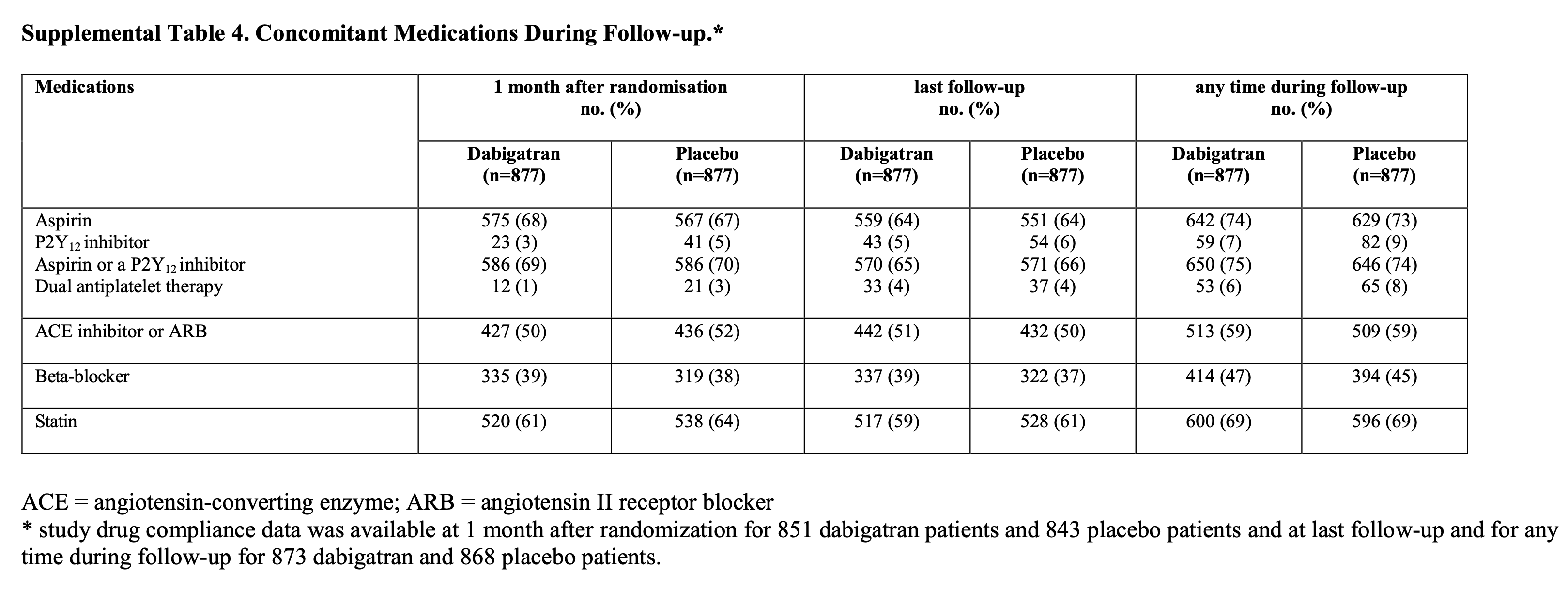
The primary outcome hazard ratio was 0·72, 95% CI 0·55–0·93; p=0·0115.
We all know that ITT analysis can be problematic in RCTs with long follow-up and/or differential non-adhrence between groups (ref 1 and ref 2). How should one interpret these results given such high non-adherence, albeit equally high in both groups?