Dear Professors and Colleagues,
We have been studying the trends in carbapenem resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa over ten years (2013-2022). P. aeruginosa is a significant cause of hospital-acquired infections, particularly in patients with compromised immune systems. We want to confirm whether our statistical procedures and conclusions are correct. Below is a summary of our methodology, results, and conclusions. We used Stata version 18.5 for all analyses. We have some specific questions that need to be addressed.
DATA OVERVIEW
Variables of interest are crp, crp_yr, and year.
fre crp year
crp -- Carbapenems-resistant?
-----------------------------------------------------------
| Freq. Percent Valid Cum.
--------------+--------------------------------------------
Valid 0 No | 1493 59.96 59.96 59.96
1 Yes | 997 40.04 40.04 100.00
Total | 2490 100.00 100.00
-----------------------------------------------------------
year -- Year of culture
-----------------------------------------------------------
| Freq. Percent Valid Cum.
--------------+--------------------------------------------
Valid 2013 | 444 17.83 17.83 17.83
2014 | 317 12.73 12.73 30.56
2015 | 255 10.24 10.24 40.80
2016 | 275 11.04 11.04 51.85
2017 | 225 9.04 9.04 60.88
2018 | 200 8.03 8.03 68.92
2019 | 251 10.08 10.08 79.00
2020 | 140 5.62 5.62 84.62
2021 | 192 7.71 7.71 92.33
2022 | 191 7.67 7.67 100.00
Total | 2490 100.00 100.00
-----------------------------------------------------------
. table year, statistic(frequency) statistic(mean crp_yr)
---------------------------------------
| Frequency Percent
----------------+----------------------
Year of culture |
2013 | 444 28.82883
2014 | 317 34.70031
2015 | 255 40.39216
2016 | 275 45.81818
2017 | 225 43.11111
2018 | 200 43.5
2019 | 251 33.06773
2020 | 140 40
2021 | 192 50
2022 | 191 58.11518
Total | 2,490 40.04016
---------------------------------------
HYPOTHESIS AND OBJECTIVES
-
Hypothesis: The resistance rate of P. aeruginosa against carbapenems has been increasing over the past ten years.
-
Objective: To assess the resistance trend over the years, determine if it is increasing or decreasing, conduct statistical analysis to confirm the trend, and quantify it if possible.
RESULTS
- Kendall’s Rank Correlation
. ktau year crp_yr
Number of obs = 2490
Kendall's tau-a = 0.5221
Kendall's tau-b = 0.5867
Kendall's score = 1617933
SE of score = 40867.128 (corrected for ties)
Test of H0: year and crp_yr are independent
Prob > |z| = 0.0000 (continuity corrected)
Interpretation: There is a significant positive correlation between year and carbapenem-resistant percentage.
- Cochran-Armitage Test for Trend
. nptrend crp, group(year) carmitage exact
Cochran–Armitage test for trend
Number of observations = 2,490
Number of groups = 10
Number of response levels = 2
--------------------------------------------------------
| Mean
| response Number
Group | Group score score of obs
-------------+------------------------------------------
year |
2013 | 2013 .2882883 444
2014 | 2014 .3470032 317
2015 | 2015 .4039216 255
2016 | 2016 .4581818 275
2017 | 2017 .4311111 225
2018 | 2018 .435 200
2019 | 2019 .3306773 251
2020 | 2020 .4 140
2021 | 2021 .5 192
2022 | 2022 .5811518 191
--------------------------------------------------------
Statistic = 0.0211869
Std. err. = 0.0033507
z = 6.323
Prob > |z| = 0.0000
Exact prob = 0.0000 (10,000 Monte Carlo permutations)
Test of departure from trend:
chi2(8) = 31.75
Prob > chi2 = 0.0001
Interpretation: There is a significant increasing trend in carbapenem resistance, which is not linear.
- Nonlinear Spline Model
Given that the relationship between resistance and time is not linear, we fit a cubic spline-restricted linear regression model.
mkspline spl_year = year, cubic
regress crp_yr spl_year1 spl_year2 spl_year3 spl_year4
Source | SS df MS Number of obs = 2,490
-------------+---------------------------------- F(4, 2485) = 12987.82
Model | 164363.211 4 41090.8028 Prob > F = 0.0000
Residual | 7862.02978 2,485 3.16379468 R-squared = 0.9544
-------------+---------------------------------- Adj R-squared = 0.9543
Total | 172225.241 2,489 69.1945525 Root MSE = 1.7787
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
crp_yr | Coefficient Std. err. t P>|t| [95% conf. interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
spl_year1 | 4.364291 .1364428 31.99 0.0000 4.096737 4.631844
spl_year2 | 51.64248 2.319006 22.27 0.0000 47.0951 56.18986
spl_year3 | -135.0883 4.033898 -33.49 0.0000 -142.9985 -127.1782
spl_year4 | 155.7053 2.331507 66.78 0.0000 151.1334 160.2772
_cons | -8756.335 274.713 -31.87 0.0000 -9295.025 -8217.645
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Model Comparison:
The table below presents the R-squared, AIC, and BIC values for the different models compared:
Model | R-squared | AIC | BIC |
|----------------------|-----------|----------|----------|
| Cubic Spline | 0.9465 | 10342.4 | 10371.5 |
| Cubic Polynomial | 0.8712 | 12527.16 | 12527.16 |
| Fractional Polynomial| 0.6763 | 14820.53 | 14837.99 |
| Quadratic Polynomial | 0.5538 | 15619.66 | 15637.12 |
Interpretation: The cubic spline model showed significant coefficients for each term, indicating a good fit with an R-squared value of 0.9544. It also confirmed the nonlinear trend over the years.
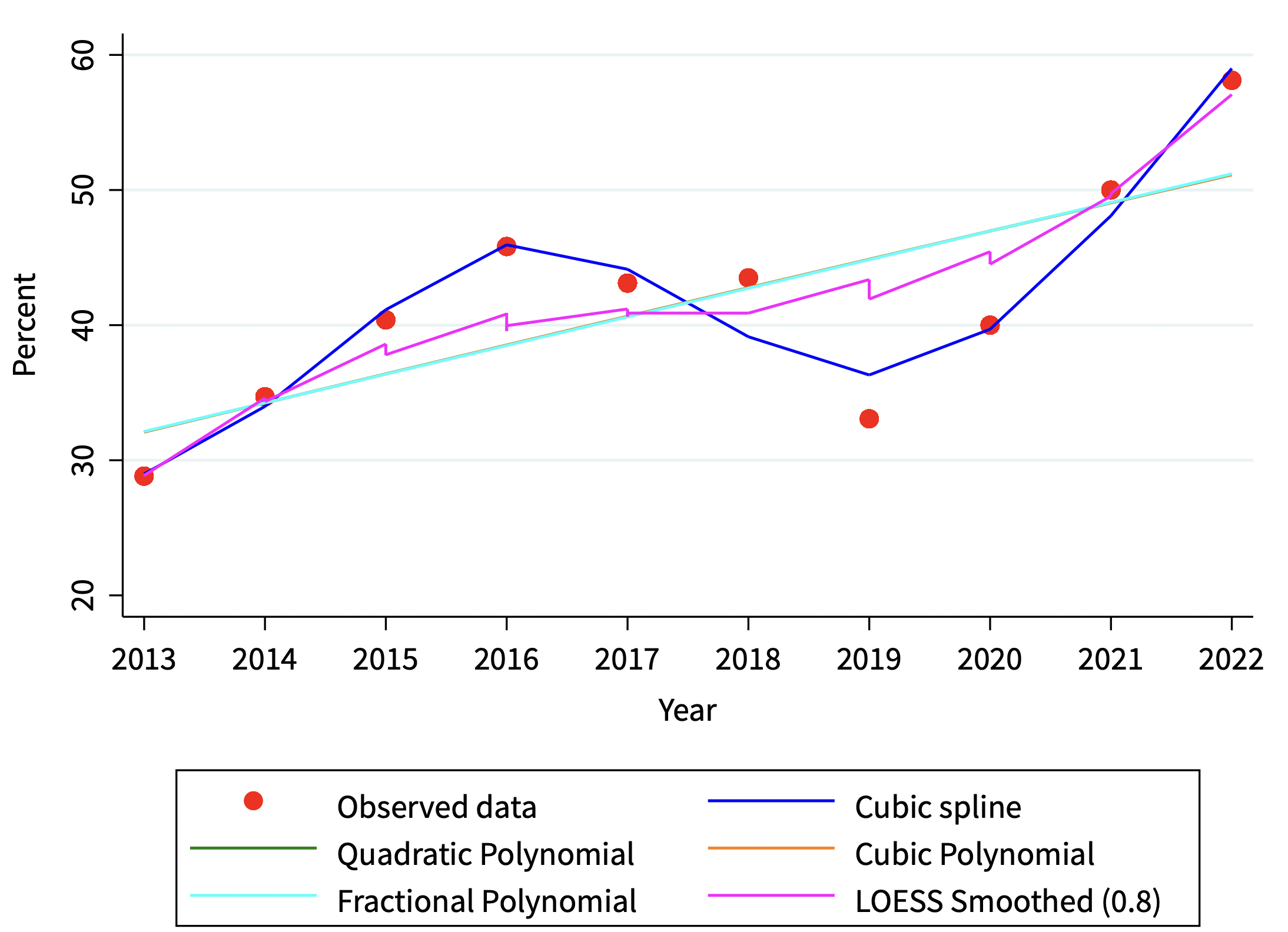
CONCLUSION AND QUESTIONS
The resistance rate of P. aeruginosa against carbapenems has significantly increased over the past ten years. The cubic spline model was the best model for capturing this nonlinear trend.
AI Models’ Recommendations:
We consulted multiple AI models (GPT-4, Llama 3.1, Perplexity Pro, Claude Sonnet 3.5, and Gemini 1.5 Pro), and most of them recommend the following:
-
Generalized Additive Models (GAMs):
Consider using GAMs for a flexible alternative to spline models, allowing for automatic selection of the degree of smoothing. -
Predicted Rates:
Calculate predicted resistance rates at key points (e.g., start, middle, and end of the study period) to quantify the change over time.
Questions
We are concerned about:
- The appropriateness of using Kendall’s tau and the Cochran-Armitage test for trend.
- The interpretation of the cubic spline model and its coefficients.
- Do you agree with the AI models’ suggestions, and should we consider implementing them, specifically the GAM model?
- How can the resistance rate be accurately quantified over the years? For instance, can we say the resistance rate is increasing by approximately xx.xx% per year based on the cubic spline model or any other suggested model?
Final Note:
We came across a post by @f2harrell, which was very informative and made us unsure about using AI models to run our analysis.
We appreciate any help you can provide.
Abdullah